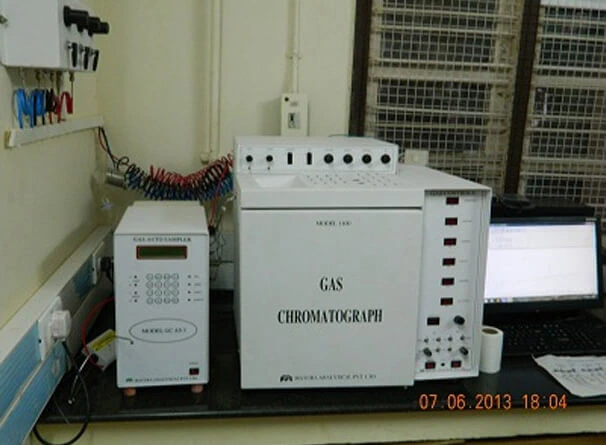
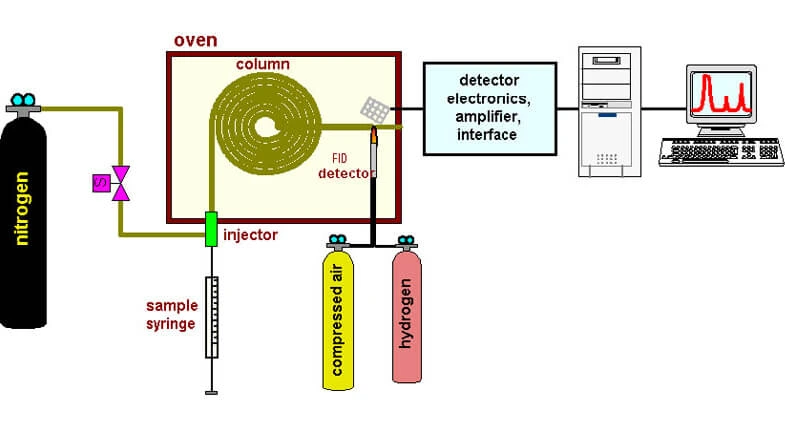
Gas Chromatograph
Gas Chromatography (GC) also sometimes known as Gas-liquid chromatography (GLC) is a separation technique in which the mobile phase is a gas. Gas chromatography is always carried out in a column, which is typically ‘packed’ or ‘capillary’. GC involves a sample being vaporized and injected onto the head of the chromatographic column. The sample is transported through the column by the flow of inert, gaseous mobile phase. The column itself contains a liquid stationary phase which is absorbed onto the surface of an inert solid. Commonly used carrier gases include helium, nitrogen, argon and carbon dioxide. The choice of carrier gas is often dependent upon the type of detector which is used. The carrier gas system also contains a molecular sieve to remove water and other impurities.
The split/split less sample injection port ensures that the sample introduced onto the capillary column is not too large and enters the column as a plug of vapor. The most common injection method is using a micro syringe through a rubber septum into a flash vaporizer port at the head of the column. Gas chromatography uses many types of detectors and the commonly used detector is Flame Ionization Detector (FID) and Thermal Conductivity Detector (TCD). Different detectors provide different selectivity. The FID is a useful general detector and is mass sensitive rather than concentration sensitive. This gives the advantage that changes in mobile phase flow rate do not affect the detector’s response. The FID detector is very sensitive and is used for analysis of organic compounds. It has a large linear response and low noise. It is robust and easy to use but it unfortunately destroys the sample.